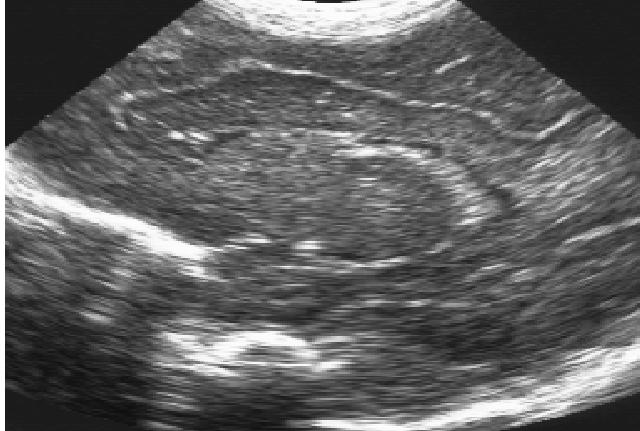
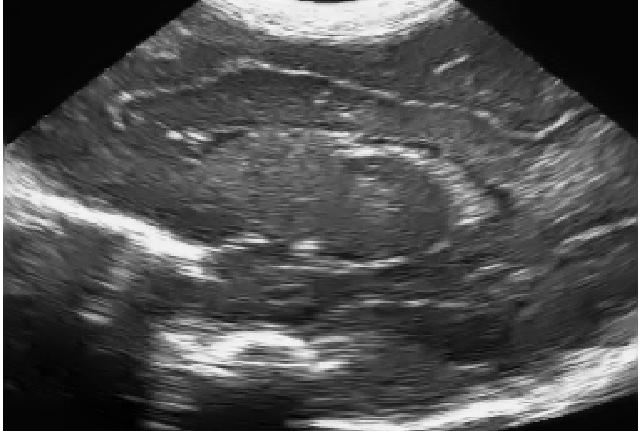
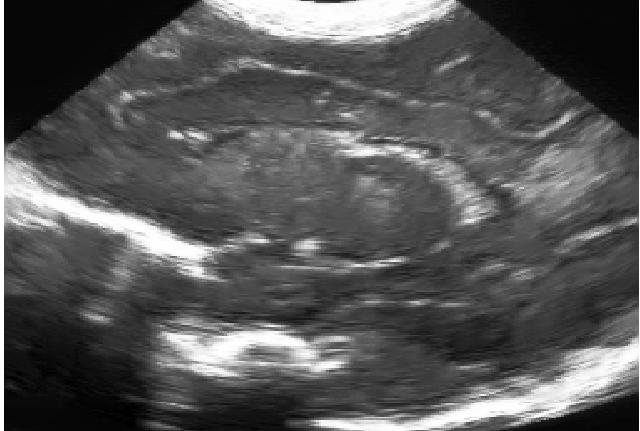
Original ultrasound image, and two results with different amount of smoothing.
A tunable parameter T exists. The final choice here is up to the medical expert.
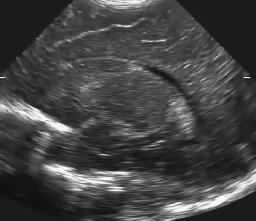
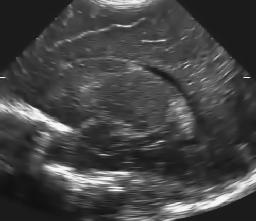
Left to right: original ultrasound image, and two results with different amount of smoothing (T=2 and T=4).
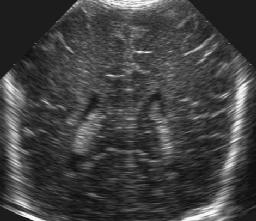
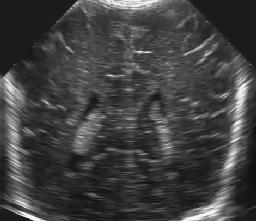
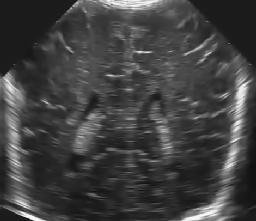
Left to right: original ultrasound image, and two results with different amount of smoothing (T=2 and T=4).
The parameter value can be fixed to the value that maximizes the signal to noise ratio. The method operates then fully automatically.
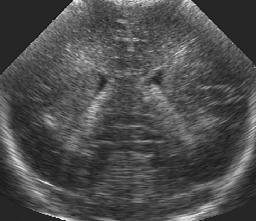
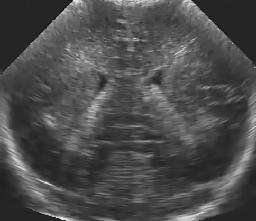
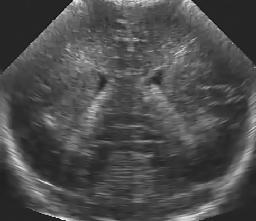
Left: original. Middle: homomorphic Wiener. Right: the proposed method.
In this example, the test image is artifficially corrupted by spatially correlated synthetic speckle.
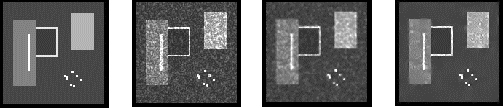
Left to right: noise-free image, artificial speckle (sigma=0.9), the results of the homomorphic Wiener and the proposed filter.